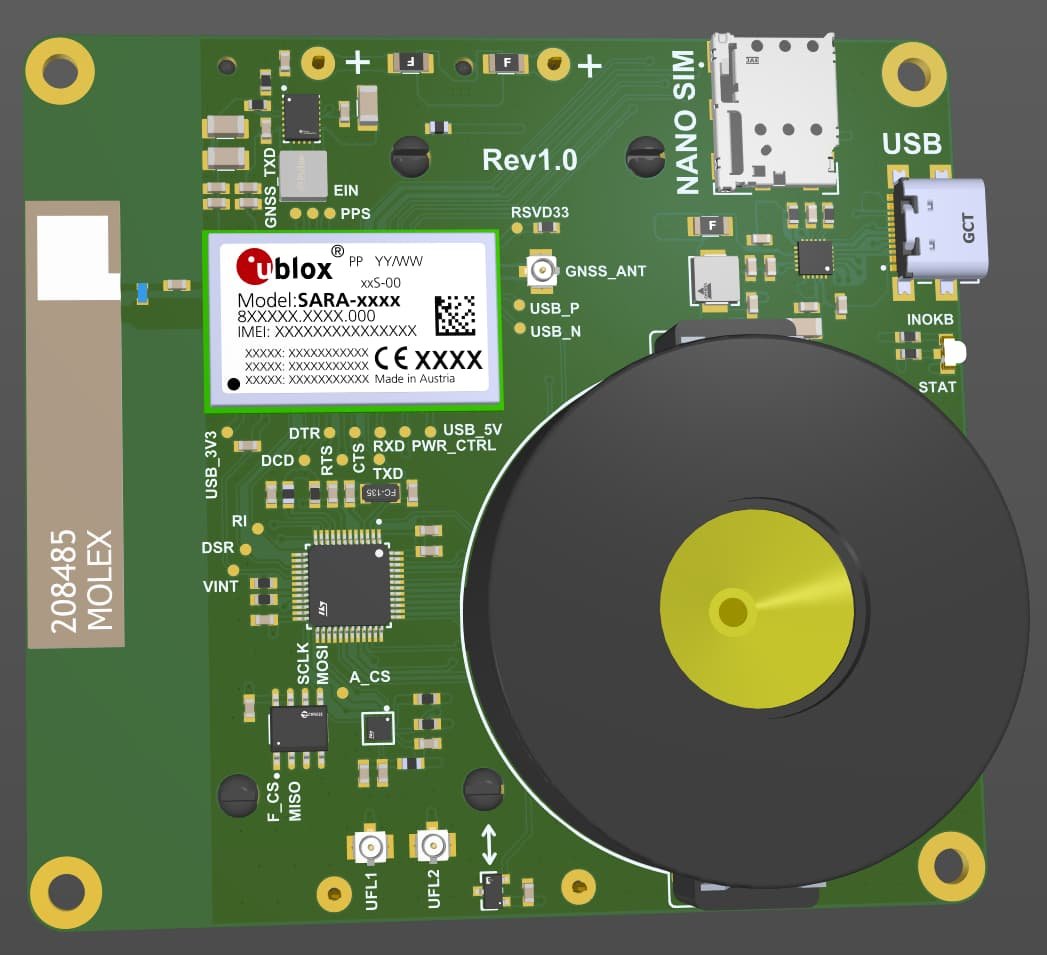
Welcome back! In our first blog post, we took a deep dive into the pinout of the original instrument cluster connector. We explored each pin and its corresponding function, gaining valuable insights that will help us as we move forward with our project to create a digital instrument cluster.
If you haven’t read the first post about this instrument cluster project, you can find it here.
In this second blog post, we will take a closer look at the remaining functions of the instrument cluster and discuss what additional functions we want to add to our digital instrument cluster. With a clear understanding of the original functions and a plan for new ones, we will be well on our way to creating a modern digital instrument cluster.
Additional features of the Kawasaki z1000 instrument cluster
When it comes to motorbike instrument clusters, there isn’t usually a lot to talk about. This is especially true when dealing with an older instrument cluster like the one on the 2006 Kawasaki Z1000 (Figure 1). While our first blog post explained the pinout and operations of the original instrument cluster, there are a few more features to go through. These are the odometer, trip, clock, and English/metric mode selection. Despite their simplicity, these functions are still crucial for any rider who wants to keep track of their miles, monitor their trip progress, and ensure that they are on time for their next destination. As we move forward with our project, we will use these functions as a starting point and build upon them to create a more advanced and feature-rich instrument cluster.

Odometer, Trip, Clock and English/metric mode selection
The Kawasaki Z1000 instrument cluster has two buttons: “mode” and “reset.” These are used to switch between the different functions available. The mode button allows riders to cycle through the odometer, trip, and clock functions (Figure 2). Mileage or time is displayed on the screen of the instrument cluster when one of the functions is selected. The reset button is used to reset trip data, adjust settings, or change English/metric mode, depending on the current function being displayed.
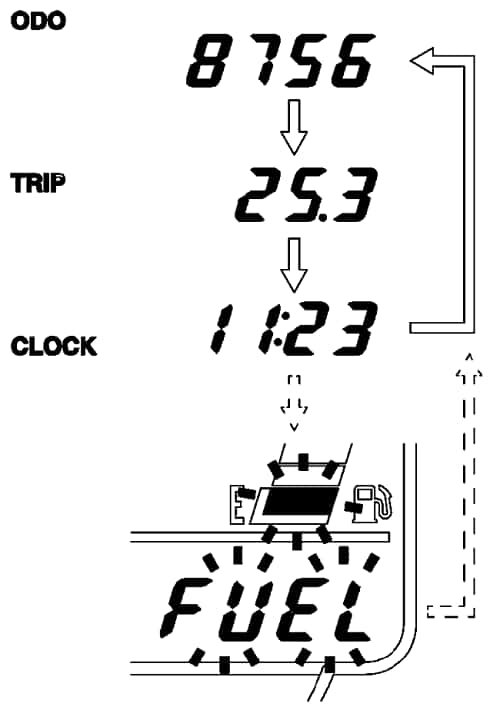
Odometer data
The odometer on a motorcycle’s instrument cluster displays the total number of miles that the motorcycle has traveled since it was first put into use. It is a standard feature on all motorcycle instrument clusters and is useful for keeping track of overall mileage. This data may be used for a variety of purposes, including tracking the motorcycle’s servicing schedule and estimating fuel economy.
Trip data
The trip meter on a motorcycle instrument cluster displays the distance traveled during a specific trip. This function is especially helpful for riders who wish to track their progress on a specific route or their fuel economy over a shorter distance. The trip meter can be reset at any time, allowing riders to start tracking a new trip whenever they like. This feature is particularly helpful for riders who like to explore new roads and routes, since it allows them to track their mileage and progress even when they are off the main road.
Clock
A motorcycle instrument cluster clock displays the current time. While this may appear to be a minor function, it is critical for riders who need to keep track of time on longer rides or during commutes. With a clear and accurate clock on their instrument cluster, riders can ensure that they arrive at their destination on time. The clock can be set manually or synced with a GPS system, depending on the specific instrument cluster.
Functions that we will add to our instrument cluster
We already discussed what functions we will replicate from the original instrument cluster, but now let’s take a closer look at the additional functions that we want to add to the instrument cluster. Let’s analyze their benefits and discuss how they can improve the safety of the motorcycle and the rider.
Information on periodic maintenance
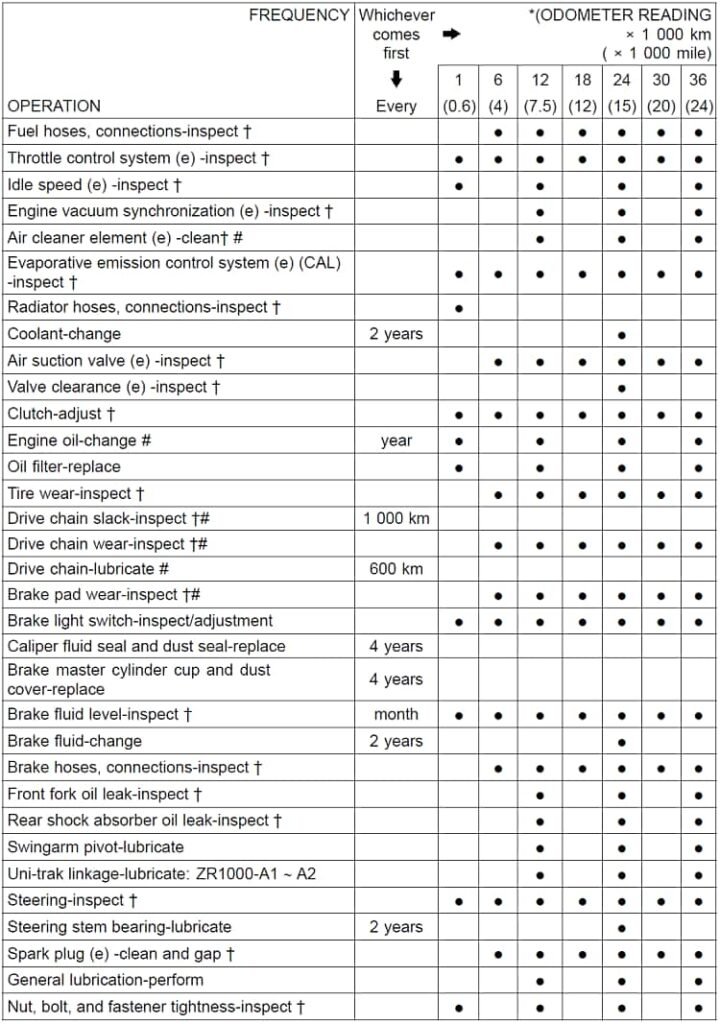
The addition of periodic maintenance information and reminders to the instrument cluster of a motorcycle can greatly improve its longevity and the rider’s safety. With this feature, the rider will be able to receive regular reminders that it is time to change the oil, check brake pads, and perform other routine maintenance tasks that are critical to the vehicle’s performance. Reminders will be able to be customized to fit the user’s preferences, and they will be able to be turned on or off as needed. This feature ensures that the user stays on top of their vehicle’s maintenance needs without having to keep track of them manually. Information on periodic maintenance for the Kawasaki z1000 can be found in the service manual. All of the operations that should be performed regularly on the motorcycle are provided in Figure 3.
GPS
The integration of GPS (GNSS) into the motorcycle instrument cluster is an innovative and practical feature that can enhance the functionality of the instrument cluster. Motorcycle riders will be able to track their motorcycles in the event of theft, providing them with peace of mind and the chance to retrieve their property, thanks to the GPS function. Furthermore, the GPS can also synchronize the clock in the instrument cluster, providing accurate and reliable timekeeping that is essential for maintaining optimal performance.
GSM
The inclusion of GSM in the motorcycle instrument cluster is a game-changing feature that enables remote communication, alarm messages, and tracking information. With this feature, riders will be able to remotely manipulate and monitor the instrument cluster. The GSM will enable the sending of alert messages in the event of theft or other situations, allowing the rider or authorities to respond quickly and effectively. Moreover, the tracking information provides riders with real-time updates on the location of their motorcycle, ensuring that they are always aware of its whereabouts. Remote communication is also quite useful, since it allows riders to communicate with their motorcycles even when they are not physically present. This allows motorcyclists to do a variety of tasks, such as monitoring the state of the vehicle and modifying various settings.
Accelerometer and gyroscope
Adding an accelerometer and a gyroscope to the motorcycle instrument cluster is a significant improvement that can increase rider safety and motorcycle security. With these sensors, the motorcycle will be able to detect whether it has been tilted or hit, providing important information to the rider about the status of their motorcycle. Moreover, the accelerometer and gyroscope may be utilized to determine whether the motorcycle has been in a collision, allowing the motorcycle to transmit an alarm message to the rider or authorities. This feature is especially valuable in emergency situations, as it can alert authorities to the location of the crash and ensure that help is dispatched quickly.
SD card
The addition of an SD card to the motorcycle instrument cluster is a useful feature that allows for the storage of data and files for future upgrades. The motorcycle instrument cluster will be able to store a variety of information and data on an SD card, including user preferences, maintenance records, and diagnostic data. Additionally, the SD card can be used to store files and media, such as music or videos.
Alarm siren
An alarm siren is an essential component of any vehicle security system. It provides an audible warning when a motorcycle is tilted or hit. The alarm siren will be designed to emit a loud, piercing sound that is intended to draw attention to the motorcycle and deter potential thieves from continuing their criminal activities. In addition to acting as a deterrent, the alarm siren can also alert the vehicle owner and nearby individuals to the attempted theft, enabling them to take action to protect the vehicle.
Gear indicator
A gear indicator is a useful feature in a motorcycle that provides riders with important information about the current gear selection. Experienced motorcycle riders usually can feel in which gear the motorcycle’s transmission is in, but nevertheless, the gear indicator is a very convenient feature. It eliminates the need for riders to guess which gear they are in, reducing the likelihood of stalling or other errors. A gear indicator is especially useful when riding in traffic or on unfamiliar roads.
Fuel consumption
The implementation of a fuel consumption calculator in the motorcycle instrument cluster is a useful feature that provides riders with important information about the fuel economy of their motorcycle. Riders will be able to track their fuel consumption over time, giving them a better understanding of their motorcycle’s performance and fuel economy. The fuel consumption calculator can be used to monitor the amount of fuel used during a specific time period as well as average fuel economy. Additionally, the fuel consumption calculator can be used to plan refueling stops, ensuring that riders have enough fuel to reach their destination without running out.
Battery voltage
A battery voltage meter might not seem that important, but it is an essential feature that provides riders with important information about their motorcycle’s electrical system. Riders will be able to check the voltage of their motorcycle’s battery in real-time using this function, allowing them to detect possible problems before they become serious issues. This information can be especially useful in situations where the motorcycle is not running, such as when it is parked or being stored for an extended period. The battery voltage meter can help riders avoid the unexpected death of a battery. This meter can be used to monitor the alternator’s health and ensure that it’s providing adequate power to the motorcycle’s electrical components.
Ambient temperature gauge
An ambient temperature gauge on a motorcycle can be a useful tool. It can warn you when temperatures are approaching freezing point, indicating the risk of ice conditions. With this feature, riders will be able to monitor the ambient temperature in real-time, enabling them to adjust their riding style for changing weather conditions. Additionally, the air temperature meter can be used to monitor the effectiveness of the motorcycle’s cooling system.
Water sensor
A water sensor can be a useful feature in a touch-screen device like a motorcycle instrument cluster. When water or moisture comes into contact with the touch screen, it can interfere with the device’s touch sensitivity and potentially cause unintended inputs or malfunctions. This can be especially dangerous for a motorcycle rider, as it can distract them from the road and potentially lead to an accident. By incorporating a water sensor into the touch screen, the device can detect when water or moisture is present and automatically lock the touch screen.
Other
We’ve been working hard on the motorcycle instrument cluster project. We’ve included things like a fuel consumption calculator, an ambient temperature meter, and even a water sensor to keep the touch screen from unintended inputs when it gets wet. Yet this is not the end of the story. I’m confident that we’ll add many more features during the design process. Ultimately, the goal of the project is to deliver a highly functional and valuable motorcycle instrument cluster that can help riders stay safe, connected, and informed on the road.